Neuherberg, 28.02.2024
Rising Focus on 'Inceptor' as a Type 2 Diabetes Therapeutic Target
Research targeting the insulin-inhibitory receptor, called inceptor, unveils promising avenues for beta cell protection, offering hope for causal diabetes therapy. A novel study in mice with diet-induced obesity demonstrates that the knock-out of inceptor enhances glucose regulation, prompting its further exploration as a drug target for type 2 diabetes treatment. These findings, led by Helmholtz Munich in collaboration with the German Center for Diabetes Research, the Technical University of Munich, and the Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich, drive advancements in diabetes research.
Targeting Inceptor to Combat Insulin Resistance in Beta Cells
Insulin resistance, often linked to abdominal obesity, presents a significant healthcare dilemma in our era. More importantly, the insulin resistance of beta cells contributes to their dysfunction and the transition from obesity to overt type 2 diabetes. Currently, all pharmacotherapies, including insulin supplementation, focus on managing high blood sugar levels rather than addressing the underlying cause of diabetes: beta cell failure or loss. Therefore, research into beta cell protection and regeneration is crucial and holds promising prospects for addressing the root cause of diabetes, offering potential avenues for causal treatment.
With the recent discovery of inceptor, the research group of beta cell expert Prof. Heiko Lickert has uncovered an interesting molecular target. Upregulated in diabetes, the insulin-inhibitory receptor inceptor may contribute to insulin resistance by acting as a negative regulator of this signaling pathway. Conversely, inhibiting the function of inceptor could enhance insulin signaling – which in turn is required for overall beta cell function, survival, and compensation upon stress.
In collaboration with Prof. Timo Müller, an expert in molecular pharmacology in obesity and diabetes, the researchers explored the effects of inceptor knock-out in diet-induced obese mice. Their study aimed to determine whether inhibiting inceptor function could also enhance glucose tolerance in diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance, both critical pre-clinical stages in the progression toward diabetes. The results were now published in Nature Metabolism.
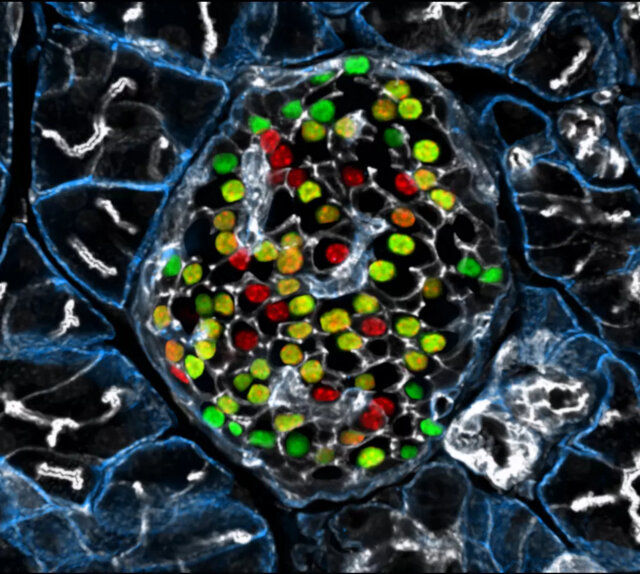
Removing Inceptor Improves Blood Sugar Levels in Obese Mice
The researchers delved into the effects of removing inceptor from all body cells in diet-induced obese mice. Interestingly, they found that mice lacking inceptor exhibited improved glucose regulation without experiencing weight loss, which was linked to increased insulin secretion in response to glucose. Next, they investigated the distribution of inceptor in the central nervous system and discovered its widespread presence in neurons. Deleting inceptor from neuronal cells also improved glucose regulation in obese mice. Ultimately, the researchers selectively removed inceptor from the mice’s beta cells, resulting in enhanced glucose control and a slight increase in beta cell mass.
Research for Inceptor-Blocking Drugs
“Our findings support the idea that enhancing insulin sensitivity through targeting inceptor shows promise as a pharmacological intervention, especially concerning the health and function of beta cells,” says Timo Müller. Unlike intensive early-onset insulin treatments, utilizing inceptor to enhance beta cell function offers promise in alleviating the detrimental effects on blood sugar and metabolism induced by diet-induced obesity. This approach avoids the associated risks of hypoglycemia-associated unawareness and unwanted weight gain typically observed with intensive insulin therapy.
“Since inceptor is expressed on the surface of pancreatic beta cells, it becomes an accessible drug target. Currently, our laboratory is actively researching the potential of several inceptor-blocking drug classes to enhance beta cell health in pre-diabetic and diabetic mice. Looking forward, inceptor emerges as a novel and intriguing molecular target for enhancing beta cell health, not only in prediabetic obese individuals but also in patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes,” explains Heiko Lickert.
Original publication:
Grandl et al. 2024: Global, neuronal or beta-cell specific deletion of inceptor improves glucose homeostasis in diet-induced obese male mice. Nature Metabolism. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-00991-3
About the scientists
Prof. Heiko Lickert, Director at the Institute of Diabetes and Regeneration Research at Helmholtz Munich, Professor for Beta Cell Biology at the Technical University Munich (TUM), Researcher at the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD)
Prof. Timo Müller, Director at the Institute of Diabetes and Obesity at Helmholtz Munich, Professor at the Walther-Straub Institute for Pharmacology and Toxicology at the Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich (LMU), Researcher at the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD)
Helmholtz Munich is a leading biomedical research center. Its mission is to develop breakthrough solutions for better health in a rapidly changing world. Interdisciplinary research teams focus on environmentally triggered diseases, especially the therapy and prevention of diabetes, obesity, allergies and chronic lung diseases. With the power of artificial intelligence and bioengineering, the researchers accelerate the translation to patients. Helmholtz Munich has more than 2,500 employees and is headquartered in Munich/Neuherberg. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, with more than 43,000 employees and 18 research centers the largest scientific organization in Germany. More about Helmholtz Munich (Helmholtz Zentrum München Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Gesundheit und Umwelt GmbH): www.helmholtz-munich.de/en
The German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) is a national association that brings together experts in the field of diabetes research and combines basic research, translational research, epidemiology and clinical applications. The aim is to develop novel strategies for personalized prevention and treatment of diabetes. Members are Helmholtz Munich – German Research Center for Environmental Health, the German Diabetes Center in Düsseldorf, the German Institute of Human Nutrition in Potsdam-Rehbrücke, the Paul Langerhans Institute Dresden of Helmholtz Munich at the University Medical Center Carl Gustav Carus of the TU Dresden and the Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases of Helmholtz Munich at the Eberhard-Karls-University of Tuebingen together with associated partners at the Universities in Heidelberg, Cologne, Leipzig, Lübeck and Munich. www.dzd-ev.de/en